TSH
The pituitary gland produces and secretes Thyroid Stimulating Hormone, or TSH, also known as thyrotropin. The amount of thyrotropin released by the pituitary gland depends upon the amounts of free T4 and free T3 (the active forms of T4 and T3) circulating through the pituitary gland from the blood. An increase in TSH concentration therefore indicates a failure of adequate thyroid hormone production (hypothyroidism). Abnormally high concentrations of T4, as seen in hyperthyroidism (a very rare condition in the dog) will inhibit TSH secretion and cause low serum concentrations of TSH.
FT3
A free or total triiodothyronine (free T3 or total T3) test is used to assess thyroid function. It is ordered primarily to help diagnose hyperthyroidism and may be ordered to help monitor treatment of a pet with a known thyroid disorder.
FT4
This test measures the amount of the free thyroxine hormone in a blood sample. Free T4 is less affected by the presence of other illnesses or drug therapies. If the free T4 is within the normal range, then your dog does not have hypothyroidism. If the free T4 is below normal range, and your dog has supportive clinical signs, then hypothyroidism is likely.


TT4
T4 circulates in the blood in two forms; one form of the hormone is bound, or attached to proteins in the blood, while the other form circulates freely within the blood stream. Total T4 measures both forms of the hormone in a blood sample. If the total T4 concentration is well within the normal range, then your dog is not hypothyroid. If the total T4 concentration is at the low end or below the normal range, and your dog has supportive clinical signs, then hypothyroidism is likely.
TT3
This test measures the level of triiodothyronine (t3) in pet’s blood. t3 is one of two major hormones made by thyroid gland.
Progesterone
It is recognized that in the dog up to 75% of failures to conceive can be attributed to incorrect timing of breeding. The reason it is so difficult to time ovulation in the absence of hormone testing is that the stages of the canine estrous cycle vary considerably in length. For routine breedings, progesterone testing may be done every other day until a rise in progesterone >1.5 ng/mL is identified. The day of the initial rise in progesterone >1.5–2.5 ng/mL is identified as “day 0.” Breedings are then advised between days 3 through 6. An additional progesterone should be performed in 2–3 days to check that levels are >5 ng/mL, confirming ovulation. It is easy to test for and can be used to look at ovulation, parturition and other cyclical abnormalities
E2 / Estradiol
An estradiol test measures the amount of a hormone called estradiol in the blood. Estradiol is one of the main types of estrogens.

Cortisol
Measurement of basal serum or plasma cortisol concentration is used as a screening test for hypoadrenocorticism in dogs and cats. Serum cortisol estimation at different time intervals are done during Low dose dexamethasone suppression test, High dose dexamethasone suppression tests and ACTH stimulation test to identify Cushing’s disease / Addisons Disease / Pituitary or adrenal tumors
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
LH, the major luteotropic hormone in cattle [61], is responsible for stimulating luteinization of the theca and granulosa cells of the pre-ovulatory follicle into luteal cells. This assay, when used in conjunction with progesterone testing, identifies the pre-ovulatory LH surge, and thus, the time of ovulation. WITNESS® LH is also used to distinguish ovariectomized from sexually intact bitches or queens.

Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
In the female, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicles by acting directly on the receptors located on the grannulosa cells; follicular steroidogenesis is promoted and LH production is stimulated. The LH produced then binds to the theca cells and stimulates steroidogenesis. An elevated FSH indicates diminished ovarian reserve. Diminished ovarian reserve is associated with a reduced number of follicles or eggs, often of questionable quality
Testosterone
Testosterone can be measured, but interpretation can be hampered by naturally low or fluctuating levels, particularly with cryptorchidism. Stimulation with GnRH or hCG may be required to demonstrate functional gonadal tissue. The response from these tests are useful for distinguishing fully castrated males from cryptorchid males or those with testicular remnants.

Free Testosterone
Free testosterone, which measures just unbound fraction or free testosterone. Free testosterone can give more information about certain medical conditions.
Anti-mullerian Hormone
Anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) is produced by the follicles of a sexually mature ovary and Sertoli cells in a sexually mature testes. After complete ovariectomy or castration, levels of AMH decrease significantly. Intact females and cryptorchid males will have higher levels of AMH than completely desexed animals. After desexing, it is recommended to wait seven days to allow serum levels to decrease before testing to confirm ovariectomy was complete OR it might lead to ovarian remnant syndrome causing pseudo oestrous bleeding. . AMH is available for male or female cats and dogs. This test is also useful in differentiating mares with ovarian granulosa cell tumours from normal mares.
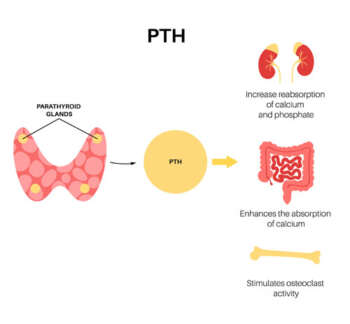
Parathormone (PTH)
A parathyroid hormone (PTH) blood test measures the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood. This test is used to help identify hyperparathyroidism, to find the cause of abnormal calcium levels, or to check the status of chronic kidney disease. PTH controls calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood.
Intact Parathormone (I PTH)
Intact PTH test is done to classify normal parathyroid gland from Hypoparathyropidism, Hyperparathyroidism, Primary and secondary aetiologies as well as Parathyroid neoplasias.
Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin therapy is the treatment of choice for non-life threatening anemia in dogs and cats with CRF when hematocrit values fall below 20% and clinical signs are attributable to the anemia. It is tested to monitor their levels during the treatment.
